Considering a hair transplant is a significant decision, often driven by concerns about hair loss and a desire to restore a fuller, more youthful appearance. As you explore this option, it’s crucial to be well-informed about the procedure, its benefits, risks, and what to expect before, during, and after. This guide aims to demystify the hair transplant process, providing you with the knowledge to make confident decisions about your hair restoration journey.
Understanding Hair Loss
Before diving into transplants, it’s helpful to understand the common causes of hair loss. The most prevalent type is androgenetic alopecia, also known as male or female pattern baldness. This genetic condition causes hair follicles to shrink over time, leading to thinner hair and eventual baldness. Other factors contributing to hair loss include stress, nutritional deficiencies, hormonal imbalances, certain medical conditions, and medications. Identifying the root cause of your hair loss with a medical professional is a vital first step.
What is a Hair Transplant?
A hair transplant is a surgical procedure that involves moving hair follicles from a denser area of the scalp (the donor area) to a bald or thinning area (the recipient area). The goal is to create a natural-looking hairline and increase hair density. The most common techniques used today are Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT) and Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE).
Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT)
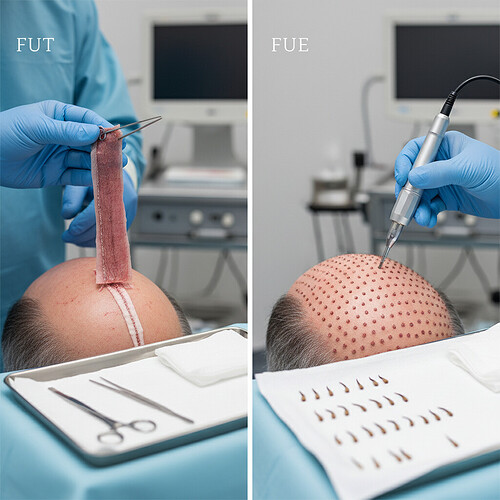
FUT, often referred to as the strip method, involves removing a thin strip of skin containing hair follicles from the donor area, typically the back or sides of the head. This strip is then dissected under a microscope into individual follicular units, which are tiny clusters of 1-4 hairs. These units are then carefully implanted into tiny incisions made in the recipient area. The main advantage of FUT is that it can yield a large number of grafts in a single session, making it efficient for covering larger areas. The primary disadvantage is the linear scar left behind in the donor area, which can be noticeable if the hair is kept very short.
Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE)
FUE is a more minimally invasive technique. Instead of removing a strip, individual follicular units are extracted directly from the donor area using a small, circular punch tool (typically 0.8-1.0 mm in diameter). These extracted units are then implanted into the recipient area. FUE offers several benefits, including minimal scarring (small, dot-like scars that are usually hidden by surrounding hair) and a quicker recovery time. However, it can be more time-consuming and may yield fewer grafts per session compared to FUT, especially for extensive hair loss.
Choosing the Right Technique
The choice between FUT and FUE depends on several factors, including the extent of hair loss, the quality and density of the donor hair, the patient’s desired hairstyle (especially regarding the length of hair in the donor area), and the surgeon’s expertise. Your surgeon will assess these factors during a consultation to recommend the most suitable technique for you.
The Hair Transplant Procedure: Step-by-Step
Regardless of the technique chosen, the general steps of a hair transplant procedure are similar:
- Consultation: This is the initial meeting with your surgeon. They will examine your scalp, discuss your hair loss history, understand your aesthetic goals, and determine your suitability for a transplant. They will also explain the different techniques, potential outcomes, and answer any questions you may have.
- Preparation: On the day of the procedure, the donor and recipient areas are prepared. The donor area is typically shaved (for FUE) or marked for the strip removal (for FUT). Local anesthesia is administered to ensure comfort throughout the procedure.
- Graft Harvesting: This is where the follicular units are obtained from the donor area using either the FUT strip method or FUE extraction.
- Graft Preparation: The harvested follicular units are carefully dissected and prepared under magnification to ensure they are viable for implantation.
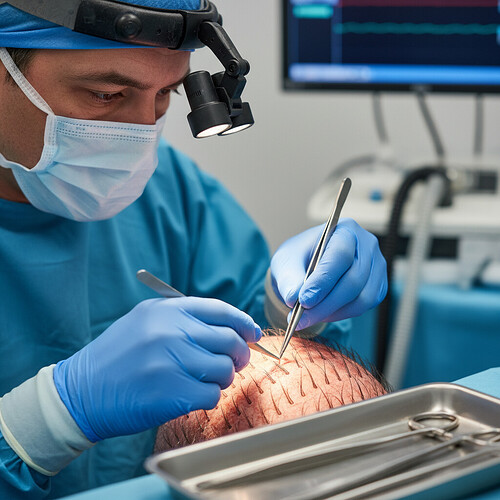
- Implantation: Tiny incisions are made in the recipient area, carefully considering the angle, direction, and density to create a natural-looking hairline. The prepared follicular units are then meticulously placed into these incisions.
- Recovery: After the procedure, the treated areas are bandaged, and you will receive post-operative instructions.
What to Expect After a Hair Transplant
Recovery varies depending on the technique used, but generally, patients can expect some swelling, redness, and discomfort in the first few days.
Potential Risks and Complications
Like any surgical procedure, hair transplants carry some risks, though they are generally considered safe when performed by qualified professionals. Potential risks include:
- Infection: Though rare, infection can occur at the graft sites.
- Swelling and Bruising: Common in the initial recovery period.
- Scarring: Linear scarring from FUT or small dot scars from FUE.
- Numbness: Temporary or, rarely, permanent numbness in the treated areas.
- Unnatural Appearance: If grafts are not placed correctly, the result may look unnatural.
- Shock Loss: Temporary shedding of existing non-transplanted hairs near the recipient area.
Choosing an experienced and reputable surgeon is the best way to minimize these risks.
Who is a Good Candidate for a Hair Transplant?
Ideal candidates for hair transplants are typically:
- Individuals experiencing progressive hair loss (androgenetic alopecia).
- Men and women with sufficient donor hair density.
- Those with realistic expectations about the outcome.
- Individuals in good general health.
- People who have tried non-surgical treatments without achieving desired results.
It’s important to note that hair transplants are not suitable for everyone. Individuals with very limited donor hair, certain scalp conditions, or those who are not healthy enough for surgery may not be good candidates.
The Importance of Choosing a Qualified Surgeon and Clinic
The success of a hair transplant largely depends on the skill and experience of the surgeon and the clinic. A qualified surgeon will have extensive training in hair restoration surgery, a deep understanding of hair growth cycles, and an artistic eye for creating natural hairlines.
- Board Certification: Ensure the surgeon is certified by a reputable medical board.
- Experience: How many hair transplant procedures has the surgeon performed?
- Specialization: Does the surgeon focus primarily on hair restoration?
- Patient Reviews and Before/After Photos: Examine testimonials and visual evidence of their work.
- Clinic Accreditation: Ensure the clinic adheres to high standards of safety and hygiene.
Cost of Hair Transplants
The cost of a hair transplant can vary significantly based on the extent of hair loss, the number of grafts needed, the technique used, the surgeon’s fees, and the geographic location of the clinic. It’s important to discuss pricing during your initial consultation and understand what is included in the overall cost.
Conclusion
A hair transplant can be a life-changing procedure for many, offering a permanent solution to hair loss and restoring confidence. By understanding the different techniques, the procedure itself, recovery expectations, and the critical importance of selecting a qualified professional, you can approach your hair restoration journey with informed optimism. Remember, thorough research and open communication with your chosen surgeon are key to achieving the best possible results.