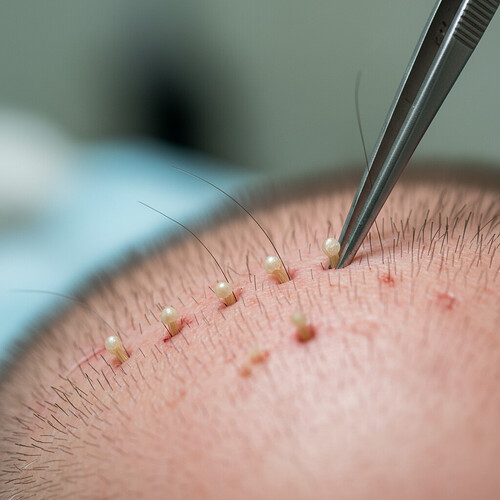
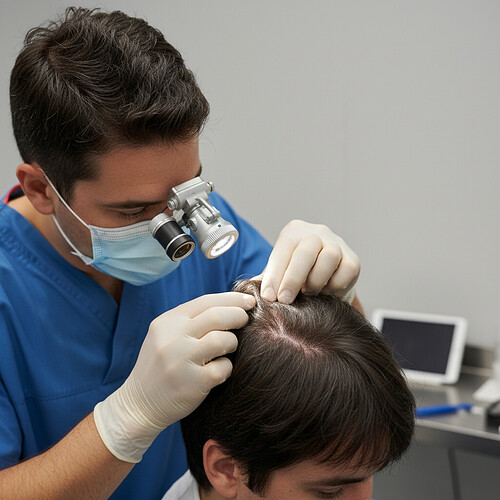
A hair transplant can be a life-changing procedure, restoring confidence and a more youthful appearance for many. However, not all hair transplant procedures yield the desired results. Sometimes, due to various factors, a hair transplant can look unnatural, sparse, or simply not meet the patient’s expectations. Fortunately, hair transplant correction, also known as revision hair transplant surgery, offers a solution for those unhappy with their initial outcome. This guide will delve into why correction surgeries are necessary, what they entail, and what you can expect.
Key Considerations for Hair Transplant Correction:
- Understanding the Reasons for Correction: Identifying the issues with the original transplant is the first step.
- Types of Revision Procedures: Learning about the different surgical techniques available.
- The Consultation Process: What to discuss with your surgeon about your concerns and goals.
- What to Expect During and After Surgery: Understanding the recovery and healing timeline.
- Choosing the Right Surgeon: The importance of selecting an experienced professional for revision.
Why Are Hair Transplant Corrections Necessary?
Several factors can lead to an unsatisfactory hair transplant result. Understanding these reasons can help individuals assess their situation and determine if a revision procedure is appropriate:
- Unnatural Hairline Design: A common issue is a hairline that is too low, too high, too straight, or has an unnatural shape. A well-designed hairline is crucial for a natural appearance, mimicking the original pattern and considering facial symmetry. An poorly designed hairline can make the transplant look obvious and artificial.
- Poor Graft Placement and Density: Insufficient density or grafts placed at unnatural angles can create a patchy or doll-like appearance. Grafts should be placed to follow the natural direction and angulation of existing hair for a seamless blend.
- Scarring or Poor Donor Area Management: Previous procedures might leave visible scarring in the donor area (where hair follicles are harvested), especially with older techniques like FUT (Follicular Unit Transplantation). Poor harvesting can also deplete the donor area, making future procedures difficult.
- Graft Survival Issues: In some cases, a significant number of transplanted grafts may not survive due to improper handling, poor surgical technique, or inadequate post-operative care. This results in sparse coverage and disappointment.
- Progression of Hair Loss: Sometimes, the initial transplant might have been adequate at the time, but the patient’s natural hair loss continued, leading to an unnatural contrast between transplanted and native hair. This might require additional procedures or specific management strategies.
- Infection or Complications: Although rare, infections or other surgical complications can negatively impact the outcome of a hair transplant.
Types of Hair Transplant Revision Procedures
Revision hair transplant surgery is tailored to the specific problems identified in the original procedure. The goal is to correct the flaws and achieve a more natural and aesthetically pleasing result. Common revision techniques include:
-
Corrective Hairline Design: If the hairline is unnatural, the surgeon can strategically remove grafts or transplant new ones to refine its shape, lower or raise it, and create a softer, more natural border. This often involves meticulous planning and artistry.
-
Improving Density: If the density is too low, additional grafts can be transplanted into the thinning areas. This might involve using techniques like Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT) or Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE) to harvest healthy grafts from the donor area and meticulously place them to enhance fullness.
-
Graft Relocation or Removal: In cases where grafts are placed at incorrect angles or are too close together, some grafts may need to be surgically removed or relocated to achieve a more natural look. This is a delicate procedure requiring precision.
-
Scar Revision: For visible scarring in the donor area, techniques like scar camouflage (tattooing), scar excision, or using FUE to harvest hair around the scar can help minimize its appearance.
-
Managing Shock Loss: If native hair has been lost due to the trauma of the original transplant (shock loss), revision surgery might involve transplanting new grafts into these areas once the native hair has stabilized.
The Consultation Process for Revision Surgery
A thorough consultation is the most critical step before undergoing a revision hair transplant. Here’s what you can expect:
- Detailed Discussion of Your Concerns: Be prepared to discuss what you are unhappy with regarding your previous transplant. Bring photos if possible, and clearly articulate your aesthetic goals.
- Examination of the Scalp and Donor Area: The surgeon will carefully assess the condition of your scalp, the quality and quantity of available donor hair, and the extent of any scarring from the previous procedure.
- Assessment of Previous Procedure: Understanding the type of procedure you had, how many grafts were transplanted, and where they were placed is helpful.
- Realistic Outcome Planning: The surgeon will explain what is achievable with a revision procedure, considering the limitations of donor hair and the complexity of the correction. They will propose a personalized treatment plan.
- Risk Assessment: As with any surgery, there are risks involved. The surgeon will discuss potential complications, recovery time, and expected results.
What to Expect During and After Revision Surgery
Revision hair transplant surgery is often more complex than a primary procedure due to the altered tissue and potential scarring. The process can vary depending on the technique used (FUE or FUT) and the extent of the correction required.
- During Surgery: The procedure is typically performed under local anesthesia with sedation. The surgeon will meticulously harvest grafts and place them according to the revised plan. Patience and precision are key.
- Recovery: The recovery period is similar to a primary hair transplant, but it might be slightly longer depending on the complexity. You can expect some swelling, redness, and scabbing in both the recipient and donor areas. Pain is usually manageable with prescribed medication.
- Healing and Growth: It takes time for the transplanted grafts to settle and begin growing. You will likely see initial shedding of the transplanted hairs within a few weeks, followed by new growth starting around 3-4 months post-surgery. The final results will typically be visible within 12-18 months.
Choosing the Right Surgeon for Revision Surgery
Revision hair transplant surgery requires a higher level of skill, experience, and artistic vision than a primary procedure. It’s crucial to select a surgeon who specializes in corrective procedures. Look for:
- Extensive Experience: A surgeon with a proven track record in performing revision surgeries.
- Specialization: Surgeons who focus on or have a significant portion of their practice dedicated to corrective cases.
- Artistic Eye: The ability to design natural-looking hairlines and aesthetically pleasing results.
- Patient Reviews and Before/After Photos: Examine their portfolio and read testimonials from patients who have undergone revision procedures.
Conclusion:
While the prospect of a less-than-ideal hair transplant can be disheartening, hair transplant correction offers a viable path to achieving the desired aesthetic outcomes. By understanding the causes of previous unsatisfactory results, exploring the available revision techniques, and partnering with an experienced and skilled surgeon, individuals can successfully correct faulty or unnatural hair transplant results and regain their confidence.