Embarking on the journey of hair restoration can bring about a wave of questions, and at the heart of many of these inquiries lies the concept of the ‘hair graft.’ Understanding what a hair graft is, how it’s obtained, and how it’s utilized is fundamental to grasping the entire hair transplant process. This guide aims to demystify the hair graft, providing you with the knowledge you need to make informed decisions about your hair restoration.
What Exactly is a Hair Graft?
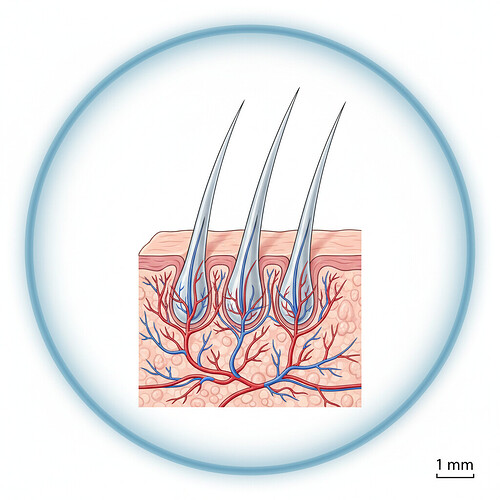
At its core, a hair graft refers to a tiny unit of tissue containing hair follicles. These follicles are the microscopic structures within the skin responsible for growing hair. A single graft can contain anywhere from one to four individual hair follicles, along with surrounding dermal cells, nerves, blood vessels, and connective tissue. The number of follicles within a graft depends on the harvesting technique used and the specific area of the scalp from which it’s taken. In the context of hair transplantation, these naturally occurring follicular units are meticulously extracted from a donor area (typically the back or sides of the head, where hair is genetically resistant to thinning) and then transplanted into the thinning or balding areas of the scalp.
The Donor Area: Where Grafts Come From
The success of a hair transplant hinges significantly on the quality and density of the donor area. The hair in the donor region, often referred to as ‘perpetual hair,’ is genetically programmed to continue growing throughout a person’s life, unlike the hair in the balding areas that is susceptible to the hormone DHT (dihydrotestosterone), which causes miniaturization and eventual hair loss. This is why surgeons carefully select and harvest grafts from these robust areas to ensure the transplanted hair will continue to grow permanently in its new location.
Harvesting Techniques: FUT vs. FUE
There are two primary methods for harvesting hair grafts: Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT) and Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE). Each has its own advantages and is chosen based on the patient’s specific needs, the extent of hair loss, and the surgeon’s expertise.
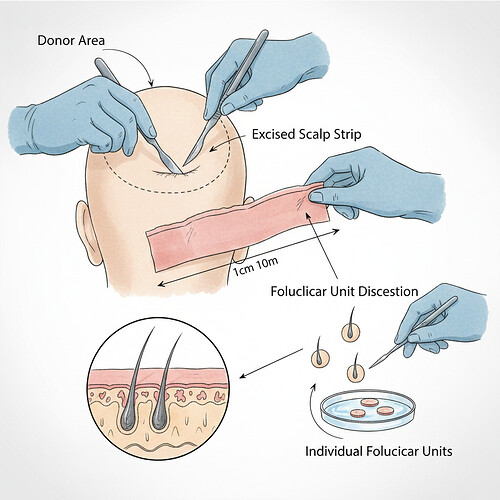
- Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT): Also known as the strip method, FUT involves surgically removing a thin strip of scalp tissue from the donor area. This strip is then meticulously dissected under high-powered microscopes by a team of skilled technicians to isolate individual follicular units (grafts). The donor area is then closed with sutures, leaving a linear scar that is typically concealed by surrounding hair once it grows out. This method can yield a large number of grafts in a single session and is often favored for covering larger areas of baldness.
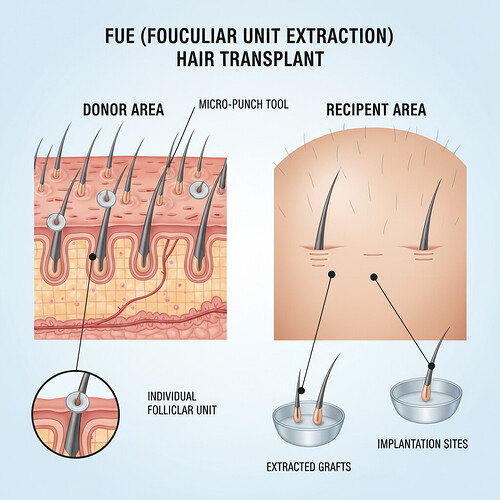
- Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE): FUE is a less invasive technique where individual follicular units are extracted directly from the donor area using tiny, specialized micro-punches (typically 0.7mm to 1.0mm in diameter). There is no need to remove a strip of tissue, resulting in multiple small, dot-like scars across the donor area, which are usually imperceptible once the hair grows. FUE allows for a more natural-looking result, particularly in cases where the patient may want to wear their hair short. It also offers faster recovery times for many patients.
Graft Preparation and Viability
Regardless of the harvesting method, the extracted grafts are incredibly delicate. Once harvested, they must be kept viable until they are implanted. This is a critical stage that requires meticulous care. Technicians meticulously sort and prepare the grafts under magnification, ensuring they are healthy and contain the correct number of follicles. They are typically stored in a special preservation solution that mimics the body’s natural environment, keeping them hydrated and nourished. The skill of the surgical team in handling these grafts directly impacts their survival rate and, consequently, the final outcome of the transplant.
The Transplantation Process: Placing the Grafts
Once the grafts are prepared, the surgeon begins the implantation phase. This involves creating tiny recipient sites in the thinning or balding areas of the scalp. The angle, depth, and direction of these sites are crucial for achieving a natural-looking hairline and a dense appearance. The surgeon then carefully places each graft into these pre-made sites, using specialized instruments. The goal is to place the grafts in a way that mimics natural hair growth patterns. This artistic aspect of hair transplantation is what differentiates a successful procedure from a subpar one.
Factors Affecting Graft Survival
Several factors influence the success rate of transplanted grafts:
- Donor Hair Quality: The health and density of the hair in the donor area are paramount.
- Harvesting Technique: Minimizing trauma to the follicles during extraction is essential.
- Graft Handling and Preservation: Proper storage and handling prevent damage to the follicles.
- Implantation Technique: The surgeon’s skill in creating recipient sites and placing grafts correctly plays a significant role.
- Post-operative Care: Adhering to the surgeon’s instructions regarding wound care, activity restrictions, and medication is vital for optimal healing and graft survival.
What to Expect After Transplantation
In the initial days and weeks following a hair transplant, some shedding of the transplanted hair is normal. This is often referred to as ‘shock loss’ and is part of the natural hair growth cycle. The transplanted follicles are simply preparing for new growth. New hair growth typically begins to emerge around 3-4 months post-procedure, with significant results usually visible within 12-18 months.
Conclusion
Understanding the hair graft is key to understanding the effectiveness and artistry of hair transplantation. It is the fundamental unit that, when skillfully harvested, prepared, and transplanted, can restore a fuller, more youthful head of hair. By familiarizing yourself with the process, the techniques, and the factors that contribute to success, you can approach your hair restoration journey with confidence and clarity. Always consult with a qualified and experienced hair transplant surgeon to discuss your individual needs and determine the best course of action for you.